About J. B. Grading System (JGS)
We educate our customers about our minute grading system on various factors. Due to this we can take full advantage to promote & increase our business through E-Commerce. We manufacture 0.18 cts to 20 cts and above in all Size and colors in Round, Princess, Marquise, Pear, Oval, Square Emerald, Emerald, Square Radiant, Radiant, Heart, Cushion etc. Grading is carried out according to rigorous criteria mapping with Labs of International repute & various other minute factors developed by our well Equipped Research Laboratory Team.
In our laboratory we have taken care of each C's in depth so that you can visualize the stone in front of your eyes. Our grading is based on GIA system so there is higher chance of upward color certification in other Lab. To narrow down the price band we give (+) color & (+/-) clarity grading.
BASIC SHAPES **
| Types of Diamond | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
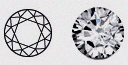
| Round - (RD) | This is by far the most popular of the shapes available today. Using precise mathematics and theories on the interplay of light, the process of producing a Round Diamond has been fine tuned for over a century to bring forth this shape's magnificent fire and brilliance. |
|
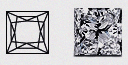
| Princess - (PR) | Just like the aura that surrounds its name, a Princess Diamond is a thing of beauty. Cut in a traditional square with pointed corners, a Princess Diamond exudes elegant brilliance and is often used to adorn an engagement ring. |
|
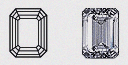
| Emerald - (EM) | The Emerald Diamond draws inspiration from the traditional pavilion cut of emerald gemstones. In the Emerald Diamond, the pavilion is cut with rectangular facets to produce a unique optical appearance, offering a larger, open table that highlights the clarity of the diamond. |
|
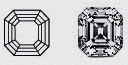
| Asscher (Square Emerald) - (SQEM) | Similar to the emerald-cut is the Asscher. Only it is square in shape. While keeping to the overall emerald-cut, the pavilion is faceted to produce a unique refractive appearance. |
|
| Marquise - (MQ) | The Marquise brings to mind the sophistication and elegance of the French. Born of nobility, this shape is perfect for long slender fingers and gives the illusion of largeness in comparison to other diamonds. A Marquise Diamond often looks stunning when it is set with Round or Pear-shaped side stones. |
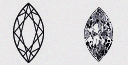
|
| Oval - (OV) | Oval Diamonds are highly regarded for their inner brilliance and eye-catching shape. Especially when languidly flashed from slender fingers. |
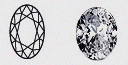
|
| Square Radiant - (SQRT) | While all Radiant Diamonds do not have precisely the same shape, the Square Radiant Diamond is distinctly square in its silhouette. One of the most preferred types in jewelry, it's even shape and signature trimmed corners work well when set with side-highlight diamonds such as Baguettes or Round Diamonds. |
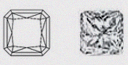
|
| Radiant - (RT) | At first glance you may be surprised. Here is a diamond shape that somehow had its corners trimmed off! But this is precisely the signature of a Radiant. A popular and versatile choice for jewelry, the radiant-cut looks equally beautiful set with either baguette or round side-diamonds. Radiant-cut diamonds can vary in their degree of being rectangular. |
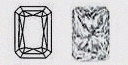
|
| Pear - (PS) | As sparkling as a falling tear. As softly rounded as a Pear fruit. This is the sweet and elegant Pear Diamond shape. This shape is often chosen for its romantic appeal as well as its flaring design. An elongated Pear Diamond shape creates a subtle slimming effect on fingers. |
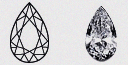
|
| Heart - (HRT) | The symbol of love. This is a choice for the romantic. A Heart Shape speaks of love like no other. A distinct and purpose-derived shape, the Heart Shape is often the lover's preferred diamond gifting choice. |
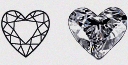
|
|
Cushion Brilliant(CUBR)
Cushion (CU) Cushion Modified Brilliant (CUMBR) |
Also known as a 'Pillow-cut', Cushion Shape diamonds have rounded corners and larger facets that increase their brilliance. Cushion Shape diamonds are available in a variety of shapes including square and rectangular. |
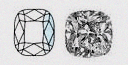
|
|
Triangle (TA)
Trilliant (TR) |
A shape that fits all occasion and reason. This shape is often chosen for its romantic appeal as well as its flaring design. A popular and versatile choice for jewelry. TA contains 22 facets while TR contains 43 facets. |
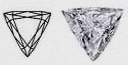
|
| Fancy Shape (FS) | This is something special, fancy shapes are shape that are carved and made keeping an inspiration in mind. This displays the creativity of the craftsman. |
Carat
- 1 carat is equal to 0.2 grams, or 0.007 ounces
- 5 carats is equal to 1 gram
- 141.7 carats is equal to 1 ounce
- There are 100 points in 1 carat. For instance, 0.33 carats is generally expressed as 33 points, or 1/3 of a carat.
| Price consideration with Size Range | Weight (unit): 1ct=100 cents 5cts = 1.000gms |
|---|---|
| 0.15 | 0.15 - 0.17 |
| 0.18 | 0.18 - 0.22 |
| 0.23 | 0.23 - 0.29 |
| 0.30 | 0.30 - 0.39 |
| 0.40 | 0.40 - 0.44 |
| 0.46 | 0.45 - 0.49 |
| 0.50 | 0.50 - 0.59 |
| 0.60 | 0.60 - 0.69 |
| 0.70 | 0.70 - 0.74 |
| 0.75 | 0.75 - 0.79 |
| 0.80 | 0.80 - 0.89 |
| 0.90 | 0.90 - 0.99 |
| 1.0 | 1.00 - 1.19 |
| 1.20 | 1.20 - 1.49 |
| 1.50 | 1.50 - 1.69 |
| 1.70 | 1.70 - 1.99 |
| 2.00 | 2.00 - 2.99 |
| 3.00 | 3.00 - 3.99 |
| 4.00 | 4.00 - 4.99 |
| 5.00 | 5.00 - 6.99 |
| 7.00 | 7.00 - 9.99 |
| 10.00 | 10.00 - 999.99 |
Diamonds act as prisms, dividing light into a spectrum of colours and reflecting this light as colourful flashes referred to as a diamond's 'fire'. The more colourless a diamond is, the more vividly colourful the 'fire' will appear. Diamonds come in every colour of the spectrum, but the most popular gems are colourless. Truly colourless, icy-white diamonds are extremely rare, and therefore, most costly. Stones are graded by colour and given designations, depending on how far they deviate from the purist white.
The best way to see the true colour of a diamond is by looking at it against a white surface. Although the majority of diamonds come in shades of white, the gems also come in a spectrum of majestic colours, from red and canary yellow to blue, green and brown. These colourful diamonds, known as fancies, are valued for their depth of colour, just as white diamonds are valued for their lack of colour.
Grades in the colour of diamonds range from D - Z. D is being truly colourless and of the highest quality. E and F are also graded as colourless while G, H, I and J are near colourless. Diamonds graded K, L and M will have obvious hints of colour and as the scale approaches P, you may find subtle changes in hue and tone. The exceptions to the rule are 'Fancy' diamonds in well-highlighted colours that include pink, blue, red, green and canary yellow. These are particularly rare and highly treasured.
We have divided color shades intensity in diamonds into three categories as:
- FAINT : Very Very Light Color Shade
- LIGHT : Light Color Shade
- STRONG : Strong Color Shade
LBR = Light Brownish Tinch
SBR = Strong Brownish Tinch
Similarly for all other shades we mention details about the tinch in three categories.
| type of colors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
It has been noticed that a stone has a colour shade apart from its actual colour. To give you a brief idea of the same, we have different colour shades:
| Types of Diamond | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| FBR - FAINT BROWNISH | These diamonds look like having a Faint brown(very light) colour inside them, which we termed as brownish shade in diamonds. |

|
| LBR - LIGHT BROWNISH | These diamonds look like having a Light brown colour inside them, which we termed as brownish shade in diamonds. | |
| SBR - STRONG BROWNISH | These diamonds look like having a brown colour inside Them, which we termed as brownish shade in diamonds. | |
| FBL - FAINT BLUEISH | These diamonds look like having a Faint bluish (Very light) colour inside them which we called as bluish shade diamonds. |

|
| LBL- LIGHT BLUEISH | These diamonds look like having a Light bluish colour inside Them, which we called as bluish shade diamonds. | |
| SBL - STRONG BLUEISH | These diamonds look like having a bluish colour inside them which we called as bluish shade diamonds. | |
| FGR - FAINT GREENISH | These diamonds look like having a Faint greenish (very light) colour in them, which we termed as green shade diamonds. |

|
| LGR - LIGHT GREENISH | These diamonds look like having a Light greenish colour in them, which we termed as green shade diamonds. | |
| SGR - STRONG GREENISH | These diamonds look like having a greenish colour in them, which we termed as green shade diamonds. | |
| FPN - FAINT PINKISH | These diamonds have Faint pinkish(very light) colour inside them called as pinkish shade diamonds. |

|
| LPN - LIGHT PINKISH | These diamonds have Light pinkish colour inside them called as pinkish shade diamonds. | |
| SPN - STRONG PINKISH | These diamonds have pinkish colour inside them called as pinkish shade diamonds. | |
| FGY - FAINT GREYISH | These diamonds have greyish colour inside them called as Faint greyish (very light) colour shade diamonds. |

|
| LGY - LIGHT GREYISH | These diamonds have greyish colour inside them called as Light greyish colour shade diamonds. | |
| SGY - STRONG GREYISH | These diamonds have greyish colour inside them called as greyish colour shade diamonds. | |
| FMT - FAINT MIX TINCH | These diamonds have Faint fancy(very light) tint inside them. |

|
| LMT - LIGHT MIX TINCH | These diamonds have Light fancy tint inside them. | |
| SMT - STRONG MIX TINCH | These diamonds have fancy tint inside them. | |
| FGB - FAINT GREENISH BROWN | These diamonds have combination of slight Faint greenish and brownish(very light) shade inside them. |

|
| LGB - LIGHT GREENISH BROWN | These diamonds have combination of slight Light greenish and brownish shade inside them. | |
| SGB - STRONG GREENISH BROWN | These diamonds have combination of slight greenish and brownish shade inside them. |





Certain diamonds are called 'Fancies'. These stones have intense natural colours that in some cases are very rare and command exceptional value. These stones are not colour graded with the scale above. Brown and yellow diamonds are the most common members of the Fancy group and have a distinct beauty of their own. Reds, blues and greens are extremely rare and highly sought after by designers and collectors. Colours are available in Blue, Brownish Pink, Greyish Black, Green Pink, Pinkish Brown, Yellowish Brown, Yellowish Green, White, Off White, Yellow and Brown.

Fancy colors are generally graded and categorized as following
| Color Grade with Hue - yellow | image |
| Faint | |
| Very Light | |
| Very Light | |
| Fancy Light | |
| Fancy | |
| Fancy Intense | |
| Fancy Dark | |
| Fancy Deep | |
| Fancy Vivid |
A diamond's clarity refers to the presence of identifying characteristics on and within the stone. While most of these characteristics are inherent qualities of the rough diamond, and have been present since the earliest stages of the crystal's growth below ground, a few are actually a result of the harsh stress that a diamond undergoes during the cutting process itself.
| Code - Shade | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| FL Flawless | Diamonds in this range have no inclusions, neither internal nor external. |
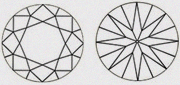
|
| IF Internally Flawless | No internal inclusions visible with 10x magnification. There may be some tiny external irregularities in the finish. |
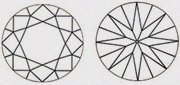
|
| VVS1 Very very slightly included 1 | Extremely difficult to see the inclusion. Even difficult to spot by trained eyes with 10 x. |
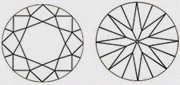
|
| VVS2 Very very slightly included 2 | Still difficult to see the inclusions with 10x magnification but easier than VVS1. |
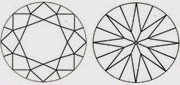
|
| VS1+ Better than VS1 & closer to VVS2 | Slightly better than VS1. |
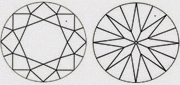
|
| VS1 Very slightly included 1 | Little difficult to see the inclusions with 10x magnification. |
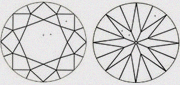
|
| VS2+ Better than VS2 & closer to VS1 | Slightly better than VS2 |
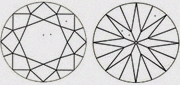
|
| VS2 Very slightly included 2 | Very small inclusions visible with 10x magnification |
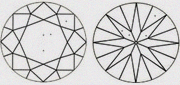
|
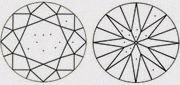
| SI1+ Better than SI1 & closer to VS2 | Slightly better than SI1. |
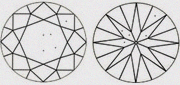
|
| SI1 Slightly included 1 | Small inclusion visible with 10x magnification. |
|
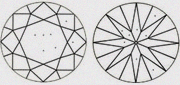
| SI1- lower than SI1 | Slightly lower than SI1 |
|
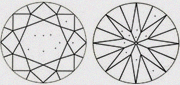
| SI2+ Better than SI2 & closer to SI1 | Slightly better than SI2 |
|
| SI2 Slightly included 2 | Small inclusions easily visible with 10x magnification. |
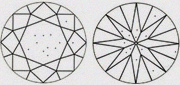
|
| SI2- lower than SI2 | Slightly lower than SI2 |
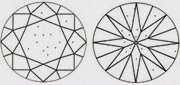
|
| SI3+ Better than SI3 & closer to SI2 | Slightly better than SI3 |
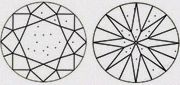
|
| SI3 Slightly included 3 | Inclusions that may be visible to the naked eye for a trained observer |
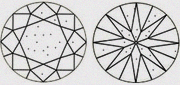
|
| SI3- Slightly lower than SI3 | Slightly lower than SI3 |
|
| I1+ Better than I1 & closer to SI3 | Slightly better than I1 |
|
| I1 Included 1 | Inclusions that may be easily visible to the naked eye for a trained observer. |

|
| I1- lower than I1 | Slightly lower than I1 |
|
| I2+ Better than I2 & closer to I1 | Slightly better than I2 |
|
| I2 Included 2 | Many flaws clearly visible to the naked eye that also decrease the brilliance |
|
| I2- lower than I2 | Slightly lower than I2 |
|
| I3+ Better than I3 & closer to I2 | Slightly better than I3 |
|
| I3 Included 3 | Many flaws clearly visible to the naked eye which decrease the brilliance and compromise the structure of the diamond, making it more easily cracked or chipped. |
|
| I3 - lower than I3 | Slightly lower than I3 |
|
To enhance our clarity grading we introduce a new factor i.e. Table Inclusion (TI). This can be Black or white inclusion on table in proportion to the clarity
| Code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| T0 - CENTER CLEAN | It doesn't have any inclusion in table. |
|
| T1 - MINOR | This inclusion is not easily visible in table and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
|
| T2 - MEDIUM | There is Slight presence of inclusion in table. It is partially visible and dependent on the clarity grade. |
|
| T3 - MAJOR | They are moderately included in table. It is visible and dependent on the clarity grade. |

|
| T4 - HEAVY | Inclusion is found in abundance in table. It is easily visible and dependant on the clarity grade. It affects the pricing of the diamond extensively. |
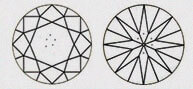
|
These ratings are dependent on the maximum inclusions for every diamond in each clarity grade and are visible with 10X magnification.
This term is used to indicate the amount of black inclusions as compared to the total inclusions in the diamond.This is sub divided in two parts 1: BIC = BLACK IN CENTER ,2: BIS = BLACK IN SIDE

| Code | Description |
Image
White Inclusions

Black inclusions

|
|---|---|---|
| B0 - NOT VISIBLE | This black inclusion is not easily visible and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
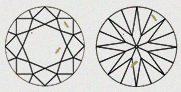
|
| B1 - MINOR | There is a Slight presence of black inclusion. This inclusion is partially visible and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
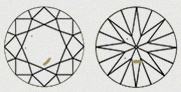
|
| B2 - MEDIUM | There is moderation of black inclusion. This inclusion is easily visible and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
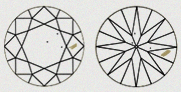
|
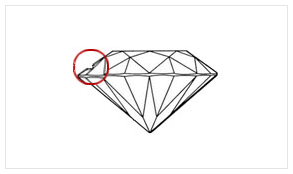
| B3 - MAJOR | Black inclusion is found in abundance. These inclusion are very easily visible and it is dependent on the clarity grade. They affect the pricing of the diamond extensively. |
|
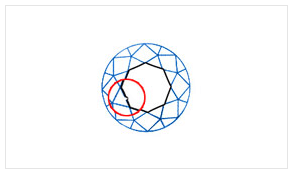
| B4 - HEAVY | Black inclusions are plenty and are clearly visible. They are instrumental in pricing of the diamond. |
|
This term is used to indicate open position in diamond if there is any open on the surface of diamonds. This is subdivided in three parts: - (1) OPTA = Open on Table, (2) OPCR = Open on Crown, (3) OPPV = Open on Pavilion.
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| (O1) - VERY SMALL | Difficult to see and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
| (O2) - SMALL | Easy to see as compared to very small and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
| (O3) - HEAVY | Easily seen and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| (O1) - VERY SMALL | Difficult to see and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
| (O2) - SMALL | Easy to see as compared to very small and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
| (O3) - HEAVY | Easily seen and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| (O1) - VERY SMALL | Difficult to see and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
| (O2) - SMALL | Easy to see as compared to very small and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
| (O3) - HEAVY | Easily seen and it is dependent on the clarity grade. |
Types of Inclusion depend upon the intensity of concentration of inclusion in entire diamond and ease of its visibility in diamonds.
| Code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| (A) Very Light of Soft | This inclusion is very soft and very light and has extremely low concentration and dependant on clarity grade. |
|
| (B) Soft | This inclusion is soft and light and has low concentration and dependant on clarity grade. |
|
| (C) Normal | This inclusion is reasonably concentrated. Clearly visible and dependant on clarity grade. |

|
| (D) Hard | This is highly concentrated. Prominently visible and dependant on clarity grade. |
|
| (E ) Very Hard | Very Highly concentrated inclusion. Very prominently visible and dependant on clarity grade. |
|
These ratings are based on the presence and intensity in the entire diamond considering the clarity grade with 10x magnification.
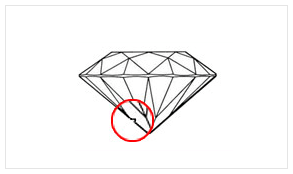
A "knot" is an included diamond crystal that extends to the surface of the diamond. In other words, it is a diamond crystal which reaches the polished surface of a finished diamond. With proper lighting and magnification you may be able to see the boundary between the knot and the diamond which contains it. Knots sometimes resemble raised areas on a facet surface or group of facets. Differences in the polish quality may be visible on the surface of the knot and the facet where it is located. We typically reject diamonds for this characteristic because we feel that knots provide a potential durability risk to the longevity of the diamond. The first picture below shows a knot as seen through our Gem Scope using a normal light source; we diffused the light source for the second picture to provide you with a different perspective of the inclusion.


| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| Y - YES | KNOT is present in diamond. |
Graining is divided in to two parts namely Internal graining (IG) and surface graining (SG). Internal inclusion of irregular crystal growth may appear milky like faint lines or streaks, or may be colored or reflective. The inclusions or graining that appears on the surface of the diamond is known as surface graining.
The comment on a lab report indicating "Internal Graining Not Shown" should not be reason for alarm because it refers to clarity characteristic which is usually not readily visible without the use of extremely high magnification. Internal Graining should not be considered an "absolute characteristic" because the visibility depends on the lighting conditions and the specific angle by which the diamond is being evaluated. It might be visible to an experience diamond grader who is examining the diamond under laboratory conditions, but may never be detected by other people. Essentially internal graining refers to part of the grain structure of the diamond which was visible as a kind of transparent line to the grader. The degree of the visibility of the grain lines will have an effect upon the clarity grade of the diamond and if no other clarity characteristics are present then the graining may be the basis for the clarity grade of the diamond. For instance, a diamond that contained small diamond crystals which by themselves would warrant a clarity grade of VS-1 might be graded as a VS-2 if internal graining were present. However another diamond that did not contain the diamond crystals might be graded as VVS-2 if the grade is based upon internal graining and the comment "clarity grade based upon internal graining" would appear under the "comments" section of the lab report while nothing is indicated under the "keys to symbols" by the plotting diagram. This series of photographs shows the very subtle effect of internal graining as seen within a diamond we purchased for inventory at various degrees of magnification. Notice how the internal graining is not readily visible in the first picture which was taken using a magnification level of about 20x. The internal graining is barely visible in the next two photographs which were taken of the table facet at about 40x magnification, the grain line appears as a kind of translucent line as indicated by the light blue arrows. We increased the magnification substantially for the remaining pictures which show the internal grain line as seen through our Gem Scope using normal and diffused light sources.

| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| IG - Internal Graining | Diamond has internal graining |
| SG - Surface Graining | Diamond has surface graining |
| Code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| E1 - Eye Clean | Diamond that has no inclusion visible to the naked eye. We describe it in clarity grade SI1 and down. Stones having clarity VS2 and above always falls in this criteria. |
|
| E2 - Semi Eye Clean | These diamonds have inclusions which are visible to trained naked eyes as compared to Eye Clean diamonds. |
|
These ratings are dependent on the maximum inclusions for every diamond in each clarity grade and visible with naked eye.
Cut (Prop)
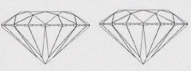
Diamond's beauty depends upon optical properties such as high Refractive index, color dispersion, luster & high degree of clarity. We give strong thrust on cut grading. Due to well equipped manufacturing system our stones are best polished. Luster means fire of diamonds. Better the Polish, brighter & more lustrous the stone. At the time of cutting take care that the light entering from top should not be lost through the teak pavilion sides. So Customer gets to observe almost 100% light from a round brilliant cut diamond. i.e. (82-83% from total internal reflection & 17 -18 % from luster). This phenomenon is known as "LIFE". As diamond critical angle is 24*, brilliance of diamond depends upon pavilion facets & pavilion angle. Cut determines brilliance. In RBC diamond Crown facets act like small prism, which split white light. Small crown gives less Dispersion & more Brilliance vice versa.
Lay people often confuse a diamond's SHAPE with its CUT; this is most likely due to the industry's synonymous use of the terms "cut" and "shape" to describe a diamonds shape (outline), i.e. marquise cut, round brilliant cut, or pear shape. In reality when we refer to the "cut" or "make" of a diamond, we are really referring to a compilation of three factors. It's PROPORTIONS in terms of degrees and percentages... the quality of its POLISH or finish... and the SYMMETRY of its facets... These three factors result in the "Overall Cut Grade" of the diamond.
| Code - Cut | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| (ID) IDEAL | Ideal cut diamonds are round diamonds that have been cut to exact, mathematical proportions. It must be symmetrical, and have 58 facets, placed exactly according to formula. These diamonds are cut to maximize the brilliance and sparkle of the stone. |
|
|
(EX+) EXCELLENT+
(EX) EXCELLENT |
This cut is intended to maximize brilliance and is as near to ideal proportions as possible. The typically smaller table sizes of these diamonds have the added benefit of creating a great deal of dispersion - or 'fire' - as well. |
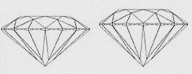
|
|
(VG+) VERY GOOD+
(VG) VERY GOOD |
This cut deviate slightly from the Excellent cut proportions in order to create a larger diamond. However, diamonds in this category reflect the majority of the light that enters them, creating a good deal of brilliance |
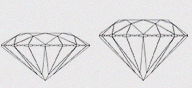
|
|
(GD+) GOOD+
(GD) GOOD |
Diamond in this category will reflect much of the light that enters them. Their proportion falls outside of the preferred range because the cutter has chosen to create the largest possible diamond. Good cut diamonds offer an excellent cost-saving without sacrificing quality or beauty. |
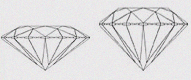
|
|
(FR+) FAIR+
(FR) FAIR |
A diamond graded as Fair will be cut to a lower standard that reflects only a small proportion of the light that enters it as compared to Good cut diamonds, losing fire and brilliance. |
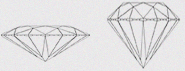
|
Polish can be result of the finishing process or be affected by blemishes created after cutting. The term "Polish" refers to the degree of "polishing lines" that appear on the surface of a finished diamond which can be seen with the use of 10x magnification. These polishing lines are caused by the minute diamond crystals which are embedded in the polishing wheels used by the diamond cutters to polish the surface of the diamond after cutting. While not quite the same in appearance, they are similar in concept to the swirl marks left on the surface of a car from the use of an orbital buffer, but are much less noticeable.
It is important to note, however, that polish lines are straight in appearance.
| Code - polish | Description |
|---|---|
| (ID) IDEAL | This is our predilection. No polish lines or marks are visible when the diamond is viewed under 10x magnification. High magnification, such as 30x may be used to locate any possible imperfections. The brilliance of a diamond with Ideal Polish will be noticeably superior to that of a diamond with a polish rating of Excellent. |
| (EX) EXCELLENT | This is our preference. No polish lines or marks are visible when the diamond is viewed under 10x magnification. High magnification, such as 30x may be used to locate any possible imperfections. The brilliance of a diamond with Excellent Polish will be noticeably superior to that of a diamond with a polish rating of Very Good. |
| (VG) VERY GOOD | Represents diamonds that contain one or two minor groupings of transparent polish lines that are visible under 10x magnification. Higher magnification will again be used to locate these areas easily. The degree of brilliance between a diamond graded as Very Good in Polish and Good is still noticeably different. |
| (GD) GOOD | Numerous areas consisting of minor transparent lines are visible under 10x magnification. Occasional white polish lines may also be visible, but limited in number. As a bare minimum, we recommend that a diamond have a Polish Grade of Good or better. However, it is important to note that it is difficult to have Excellent or Very good polish in most of fancy shape diamonds so generally it carries Good polish. |
| Code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| (ID) IDEAL | No misshapen or miss-aligned facets are visible when the diamond is viewed under 10x magnification. High magnification, such as 30x may be used to locate any mis-aligned or misshapen facets. The brilliance of a diamond with Ideal Symmetry will be noticeably superior to that of a diamond with a symmetry rating of Excellent. |
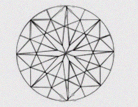
|
| (EX) EXCELLENT | No misshapen or mis-aligned facets are visible when the diamond is viewed under 10x magnification. High magnification, such as 30x may be used to locate any mis-aligned or misshapen facets. The brilliance of a diamond with Excellent Symmetry will be noticeably superior to that of a diamond with a symmetry rating of Very Good. |
|
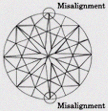
| (VG) VERY GOOD | Represents diamonds that contain one or two minor symmetry characteristics that can be found under 10x magnifications. Higher magnification will again be used by the grader to locate these areas easily. The degree of brilliance between a diamond graded as Very Good in Symmetry and one graded as having Good Symmetry is still noticeably different, however, it is practically impossible for the average consumer to distinguish between Very Good and Excellent or Ideal Symmetry without a lot of coaching. |
|
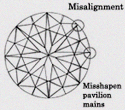
| (GD) GOOD | Numerous inconsistencies of facet alignment and shape are visible under 10 x magnifications. As a bare minimum, we recommend that a round brilliant cut diamond have a symmetry rating of Very Good or better. However, it is important to note that it is difficult to have Excellent or Very good symmetry in most of fancy shape diamonds so generally it carries Good symmetry. |

|
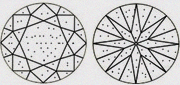
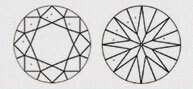
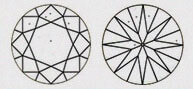
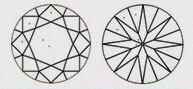
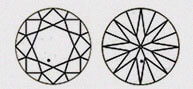
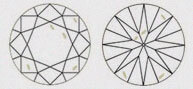
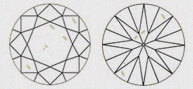
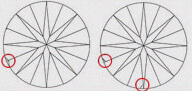
Hearts & Arrows (HA)
Faceted diamond forms a well aligned, symmetrical & balanced form that reveals the well known eight rayed arrow pattern which you can see through special device like the Fire scope by keeping diamond face up. Here symmetry pattern can be seen in perfect order. Perfect Heart shape will be observed from the pavilion side. Maximum Life, Fire, & Sparkle are observed in diamonds that has been cut, faceted in certain specific proportions. These parameters are followed by our skilled artisans.
| Code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| EX - EXCELLENT | This diamond has all its hearts and arrows in perfect shape and with accurate dimensions. It displays Very high brilliance. |

|
| VG - VERY GOOD | This diamond has most of its hearts and arrows in perfect shape and with accurate dimensions. It displays Very high brilliance but less than EXCELLENT Heart & Arrows |

|
| GD - GOOD | These diamonds will have a good number of its hearts and arrows in perfect shape and with accurate dimensions.It display Very high brilliance but less than VERY GOOD HEARTS & ARROWS. |

|
When we speak of Diamond Fluorescence, we are referring to the diamonds tendency to emit a soft colored glow when subjected to ultraviolet light (such as a "black light"). Fluorescence is a form of illumination that is created when a diamond is exposed to low or high wave ultraviolet radiation. Faint or medium fluorescence will rarely affect a diamond's appearance. Usually fluorescence is unnoticed by the human eye in ordinary light. Fluorescence can cause a diamond to appear less clear or slightly hazy if the diamond exhibits very strong or extreme fluorescence. When selecting your diamond it is best to choose a diamond that has no fluorescence or faint to moderate fluorescence.
| Code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| N - NONE | This diamond do not have any fluorescence |

|
| F - FAINT / VERY SLIGHT | This diamond have weak fluorescence, not a significant influence on color |

|
| M - MEDIUM / SLIGHT | This diamond have average fluorescence, small influence |

|
| S - STRONG | This diamond have strong influence, substantial color influence |

|
| VS - VERY STRONG | This diamond have very strong influence, substantial color influence |

|
When we speak of Diamond Fluorescence, we are referring to the diamonds tendency to emit a soft colored glow when subjected to ultraviolet light. Different diamonds emit different colors, examples of which are listed below



This is another parameter, which has been found of importance in determining the exact purity of the diamond. The amount of light that the stone reflects and the type of light that is emitted by the stone determine luster of a diamond. Luster refers to the quality of a surface in reflected light. The luster of a diamond is usually described as adamantine luster.
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| L1 - VERY GOOD | This diamond has very high quality reflection and emission of light. |
| L2 - GOOD | This diamond has high quality reflection and emission of light |
| M1 - LIGHT MILKY | This diamond has low quality reflection and emission of light |
| M2 - MEDIUM MILKY | This diamond has very low quality reflection and emission of light. |
| M3 - HEAVY MILKY | This diamond has very very low quality reflection and emission of light |
The outer edge of a diamond which forms a band around the stone. The girdle can be faceted or non-faceted.
| code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| (F) FACETED | A faceted girdle consists of a small series of polished facets. Diamond cut in a way to include many facets. The multiple facets structure increases light reflection and gives the stone a bright and shining look. |

|
| (NF ) NON-FACETED | Diamonds that do not have geometrically shaped flat polished facets are graded as non faceted |

|
A diamond's culet is the point on the bottom of a diamond's pavilion. A diamond's culet may be pointed or it may be blunted with a small facet. The culet facet can vary in size. This culet's size determines the grade that the culet is assigned.
| code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| PO - POINTED | If there culet faceted is NONE then it is referred pointed culet. The kite facets of the crown should exactly intersect with the pointed edge of the pavilion main facet and the upper girdle facet should synchronize with girdle facets. There should be a perfect alignment and no sideways displacement with respect to each other |
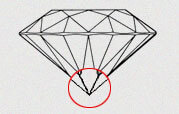
|
| MD - MEDIUM | If culet faceted is medium then it is referred as medium culet |
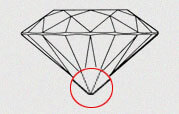
|
| FC - FACETED | If culet faceted is very high then it is referred as faceted culet. This culet should lie in the centre of the octagonal table. It is very easy to see whether the culet is eccentric from a side view of the stone as well as on looking through the table. |
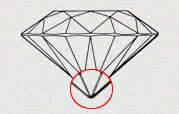
|
| BR - BROKEN | If culet facet is broken then it is referred as broken culet |
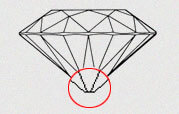
|
Extra Facets (EF)
Occasionally a cutter will find the need to remove an inclusion near the surface or to compensate for facets which do not meet correctly and he will add an "extra facet". Extra facets have no effect on clarity grades. This is subdivided in Two parts : 01) EFCR : Extra Facets on Crown, 02) EFPV : Extra Facets on Pavilion.
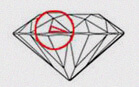
| code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| NV - NOT VISIBLE | Very difficult to find the extra facet on crown. It is not visible on crown. |
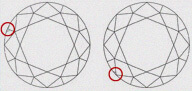
|
| MN - MINOR | Difficult to find extra facet on crown. It is slightly visible on crown with 10x magnification |
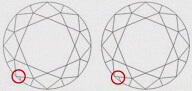
|
| MD - MEDIUM | Easy to find extra facet on crown. It is visible on crown with 10x magnification. |
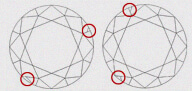
|
| MJ - MAJOR | Very easy to find extra facet on crown. It is easily visible on crown with 10x magnificationt |
|
| code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
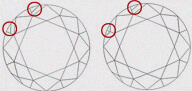
| NV - NOT VISIBLE | Very difficult to find the extra facet on Pavilion. It is not visible on Pavilion. |
|
| MN - MINOR | Difficult to find extra facet on Pavilion. It is slightly visible on pavilion with 10x magnification. |
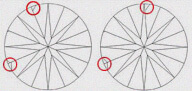
|
| MD - MEDIUM | Easy to find extra facet on Pavilion. It is visible on pavilion with 10x magnification. |
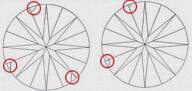
|
| MJ - MAJOR | Very easy to find extra facet on Pavilion. It is easily visible on pavilion with 10x magnification |
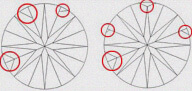
|
J.B. Grading Chart
- (BR) Brownish
- (BL) Bluish
- (GR) Greenish
- (GB) Greenish brown
- (PN) Pinkish
- (GY) Grayish
- (FT) Fancy Tinch
LBR = Light Brownish Tinch.
BR = Brownish
- FL
- IF
- VVS1, VVS2
- VS1+, VS1
- VS2+, VS2
- SI1+, SI1, SI1-
- SI2+, SI2, SI2-
- SI3+, SI3, SI3-
- I1+, I1, I1-
- I2+, I2, I2-
- I3+, I3, I3-
- (T0) Center Clean
- (T1) Minor Inclusion
- (T2) Medium Inclusion
- (T3) Major Inclusion
- (T4) Heavy Inclusion
BLACK INCLUSION ON SIDE (BIS)
- (NN) None
- (B0) Not Visible
- (B1) Minor Inclusion
- (B2) Medium Inclusion
- (B3) Major Inclusion
- (B4) Heavy Inclusion
OPEN ON CROWN (OPCR)
OPEN ON PAVILION (OPPV)
- (O1) Very Small
- (O2) Small
- (O3) Heavy
- (A) Very Light of Soft Inclusion
- (B) Soft Inclusion
- (C) Normal Inclusion
- (D) Hard Inclusion
- (E) Very Hard Inclusion
- (E1) Eye Clean
- (E2) Semi Eye Clean
- (ID) Ideal
- (EX) Excellent
- (VG) Very Good
- (GD) Good
- (FR) Fair
- (EX) Excellent
- (VG) Very Good
- (GD) Good
- (FR) Fair
HEARTS & ARROWS (H&A)
- We provide laser inscription of
- H&A in diamonds having Hearts & Arrows
- (EI) Excellent- Inscription of H&A
- (VI) Very Good- Inscription of H&A
- (GI) Good- Inscription of H&A
POLISH (PO)
- (ID) Ideal
- (EX) Excellent
- (VG) Very Good
- (GD) Good
EXTRA
PARAMETERS
EXTRA FACETS ON PAVILION (EFPV)
- (NV) Not Visible
- (MN) Minor
- (MD) Medium
- (MJ) Major
- (L1) Very Good
- (L2) Good
- (M1) Light Milky
- (M2) Medium Milky
- (M3) Heavy Milky
- (PO) Pointed
- (MD) Medium
- (FC) Faceted
- (BR) Broken
- (NN) None
- (B1) Medium
- (B2) Major
- (N) None
- (F) Faint/ Very Slight
- (M) Medium/ Slight
- (S) Strong
- (VS) Very Strong
- (Y) Yes
- (IG) Internal Graining
- (SG) Surface Graining
COLOR (FC)
- (YL) Yellow
- (BL) Blue
- (WT) White
- (OR) Orange
- (GR) Green
- (F) Faceted
- (NF) Non- Faceted

